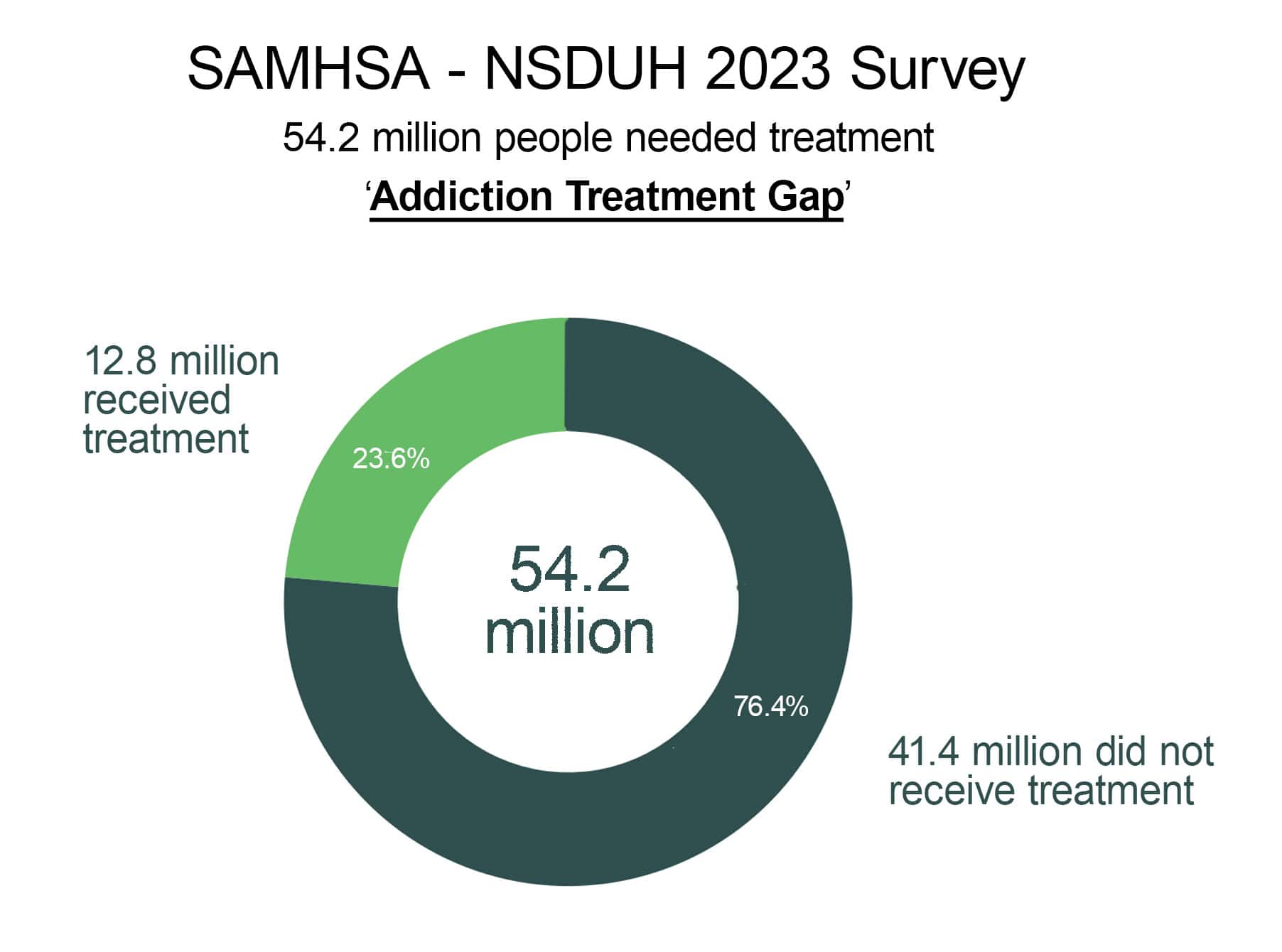
The Addiction Treatment Gap refers to the number of people having an active Substance Use Disorder that did not receive treatment for it in the past year. It refers to the difference between the number of people who need treatment for a substance use disorder and the number of people who actually receive treatment. In other words, it is the gap between the demand for and the supply of treatment services for SUD.
The vast majority of people with substance use disorders do not receive the care they need due to a range of factors, including lack of access to treatment, stigma, and limited resources. The addiction treatment gap has significant consequences, including increased rates of overdose, hospitalizations, and other negative health outcomes, as well as reduced productivity, social functioning, and quality of life.

Left untreated, Substance Use Disorders have serious consequences including: death, overdose, jail, loss of job and family, as well as mental and physical health problems. By improving access to and utilization of treatment services, a lot more people can achieve successful, long-term abstinence.
This gap exists due to a range of factors, including stigma, lack of access to treatment, and limited resources, and it has significant consequences for individuals, families, and communities.
Contributing Factors
This gap is influenced by various demographic, social, economic, and systemic factors. Here is a list of some, including:
Close the Gap Strategies
Public awareness and education about Substance Use Disorders and treatment options will help. It is also important to address the social and environmental factors that contribute to Substance Use Disorders, such as poverty, unemployment, and lack of social support. Addressing the Addiction Treatment Gap requires an all-encompassing approach, including:
By improving access to and utilization of treatment services, we can help more people with SUD achieve recovery and improve their health and well-being.
To address the treatment gap, it is important to expand access to evidence-based treatment services, reduce stigma and discrimination against people with SUD, and increase public awareness and education about SUD and treatment options. It is also important to address the social and environmental factors that contribute to SUD, such as poverty, unemployment, and lack of social support. By taking a comprehensive and integrated approach to addressing SUD, we can help close the treatment gap and improve outcomes for people with SUD.

The addiction gap is a pressing issue with widespread ramifications. Addressing it requires collective effort, innovative strategies, and a commitment to viewing addiction through a compassionate, medical lens. By understanding and confronting the causes, recognizing the costs, and implementing effective strategies, we can move closer to reducing the gap and ensuring that everyone who wants addiction treatment has access to help.
Addiction Gap is a certified 501(c)(3) nonprofit